syn·site
in contemporary art terms: a "syn-site" is a conceptual space that encapsulates a multitude of experiences, observations, and interactions across various physical and digital locales. It is a dynamic, non-singular site that challenges conventional notions of place and situates itself within the discourse of network aesthetics. Drawing upon the theories of Robert Smithson, it re-works the concept of "site" to reflect the complexity and plurality of contemporary life and artistic practice. It is an artwork and a network, a space and a memory, an assertive threshold within the syntax of site. It is both a product and a critique of the interconnected, networked nature of the contemporary world, and serves as a tool for artists to explore the entanglements of the specific and the abstract, the internal and external, the actual and the virtual.
in contemporary art terms: a "syn-site" is a conceptual space that encapsulates a multitude of experiences, observations, and interactions across various physical and digital locales. It is a dynamic, non-singular site that challenges conventional notions of place and situates itself within the discourse of network aesthetics. Drawing upon the theories of Robert Smithson, it re-works the concept of "site" to reflect the complexity and plurality of contemporary life and artistic practice. It is an artwork and a network, a space and a memory, an assertive threshold within the syntax of site. It is both a product and a critique of the interconnected, networked nature of the contemporary world, and serves as a tool for artists to explore the entanglements of the specific and the abstract, the internal and external, the actual and the virtual.
SYN (along with, at the same time | from Greek SYN, with | ~SYNTHETIC) + SITE (N: point of event, occupied space, internet address; V: to place in position | from Latin SITUS, location, idleness, forgetfulness | ~WEBSITE ¬cite ¬sight), cf. SITE/NON-SITE (from Robert Smithson, A PROVISIONAL THEORY OF NONSITES, 1968)



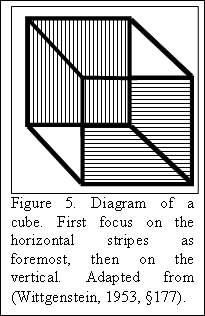
It is not the eye which sees but the body as a receptive totality.
It is not the eye which sees but the body as a receptive totality.
It is not the eye which sees but the body as a receptive totality.
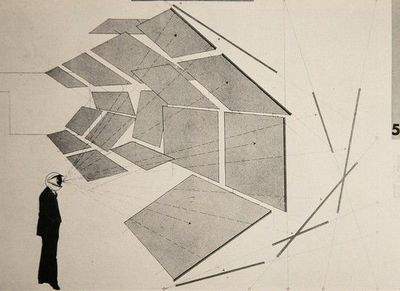




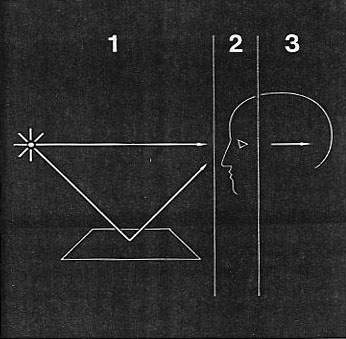


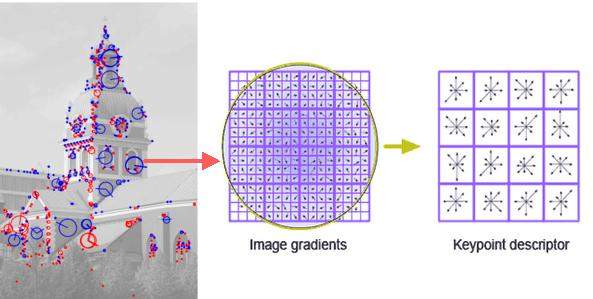


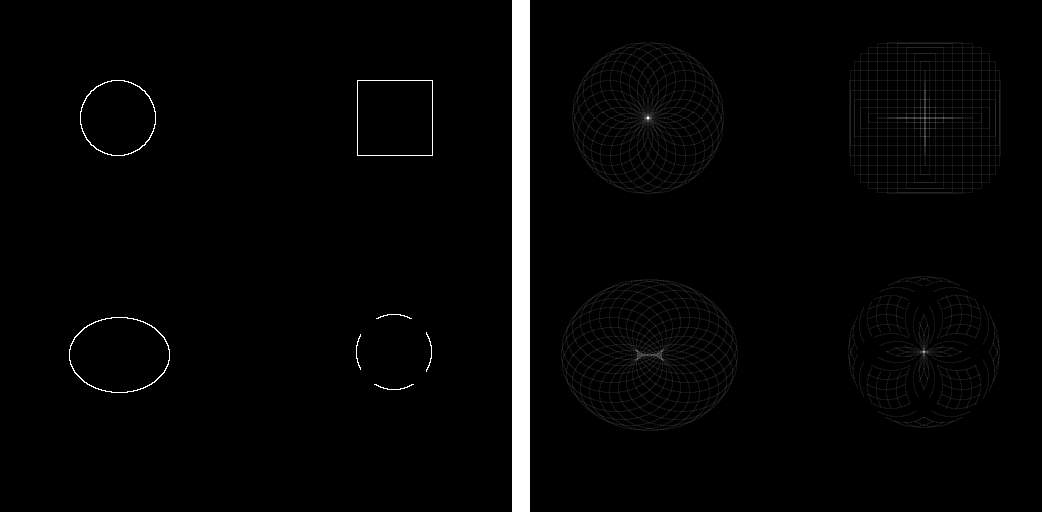


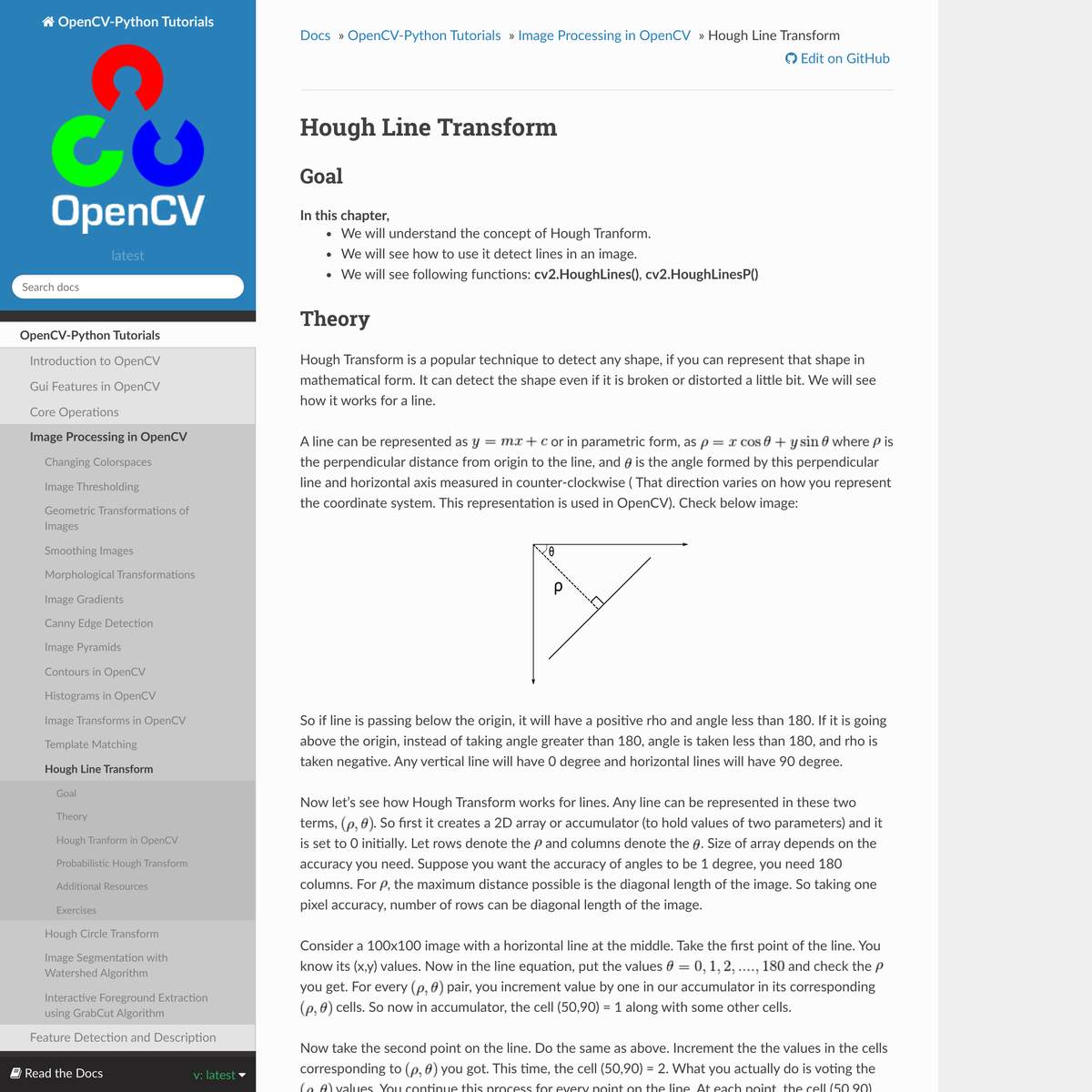

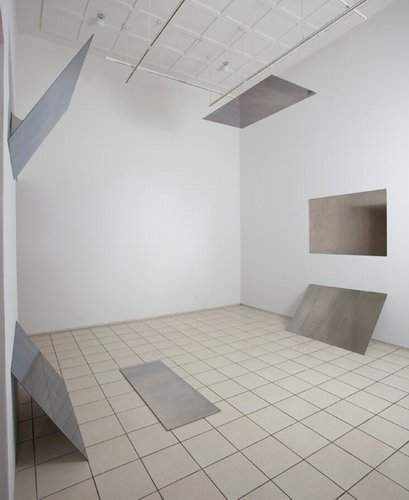
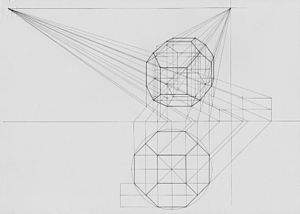
 aerial perspectives
aerial perspectives
aerial perspectives
aerial perspectives
aerial perspectives
aerial perspectives
aerial perspectives
aerial perspectives
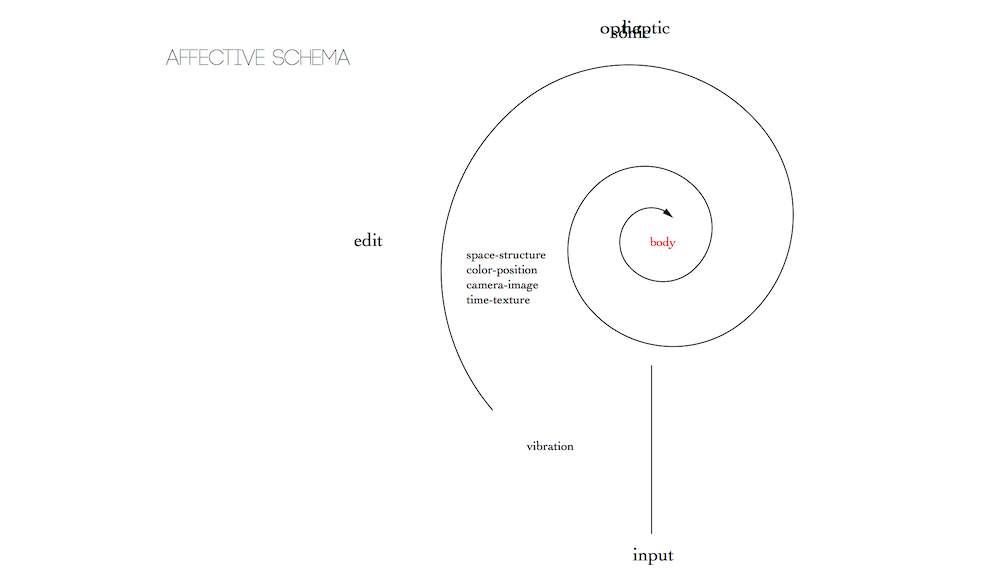








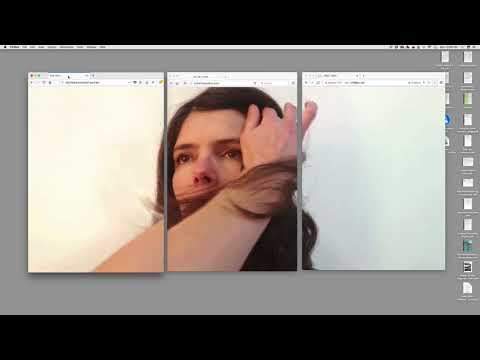


...like a piece of sensitive photographic paper, waiting passively to feel the shock of impression. And then I was quivering like a leaf, more precisely like a mute hunk of appetitional plasm, a kind of sponge in which the business of being excited was going on, run through by a series of external stimuli: the lane, the man, the pale light, the lash of silver – at the ecstatic edge of something to be known.
...like a piece of sensitive photographic paper, waiting passively to feel the shock of impression. And then I was quivering like a leaf, more precisely like a mute hunk of appetitional plasm, a kind of sponge in which the business of being excited was going on, run through by a series of external stimuli: the lane, the man, the pale light, the lash of silver – at the ecstatic edge of something to be known.
...like a piece of sensitive photographic paper, waiting passively to feel the shock of impression. And then I was quivering like a leaf, more precisely like a mute hunk of appetitional plasm, a kind of sponge in which the business of being excited was going on, run through by a series of external stimuli: the lane, the man, the pale light, the lash of silver – at the ecstatic edge of something to be known.
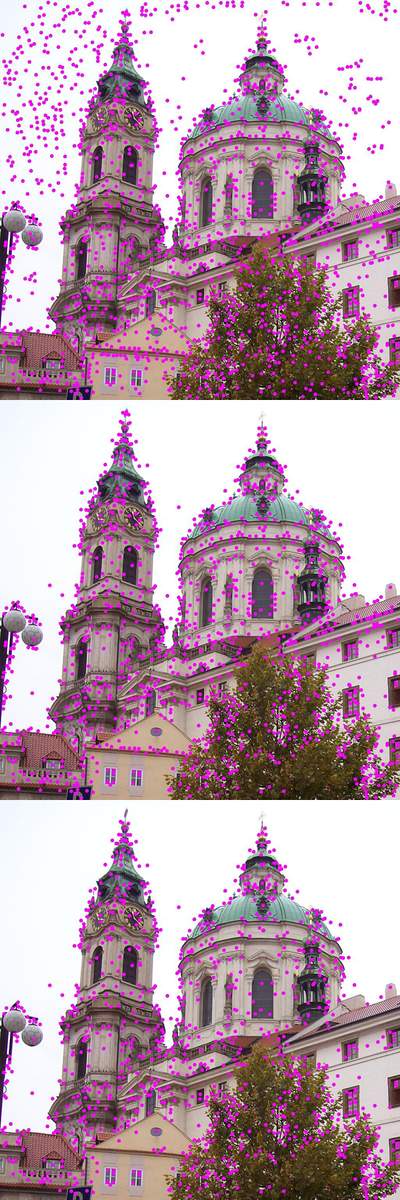
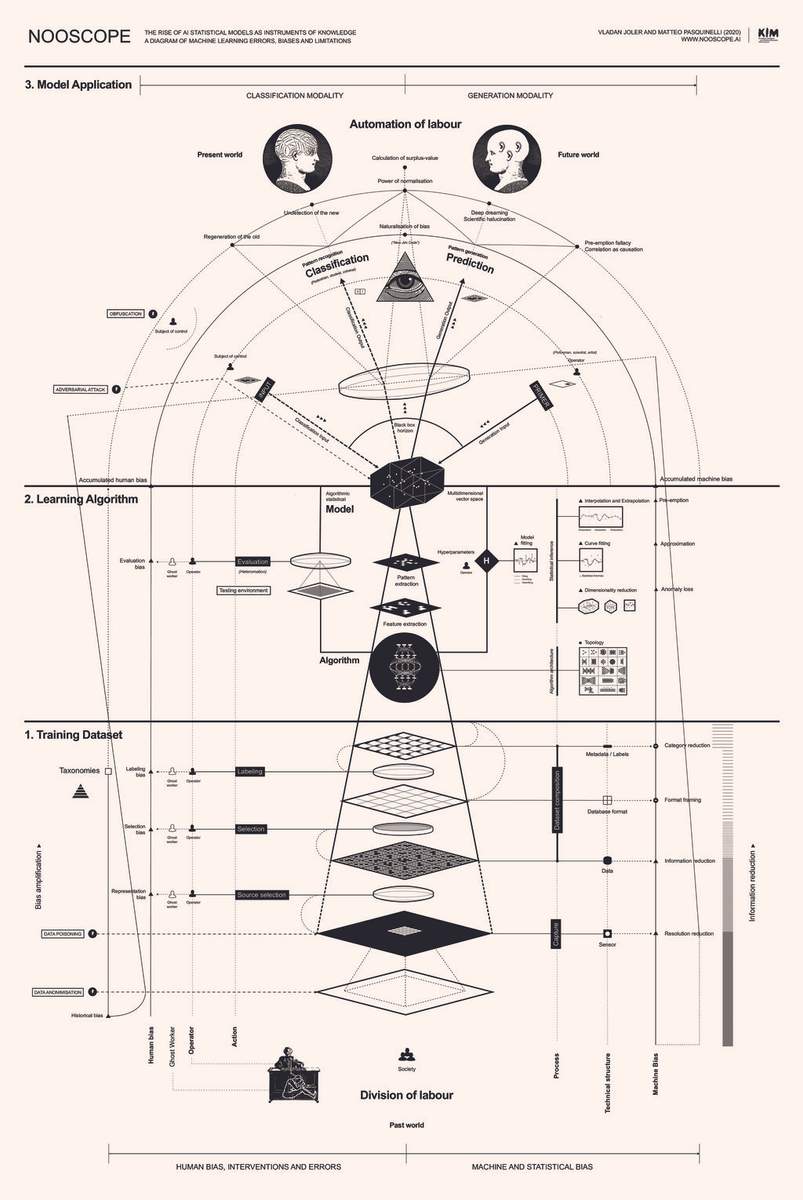





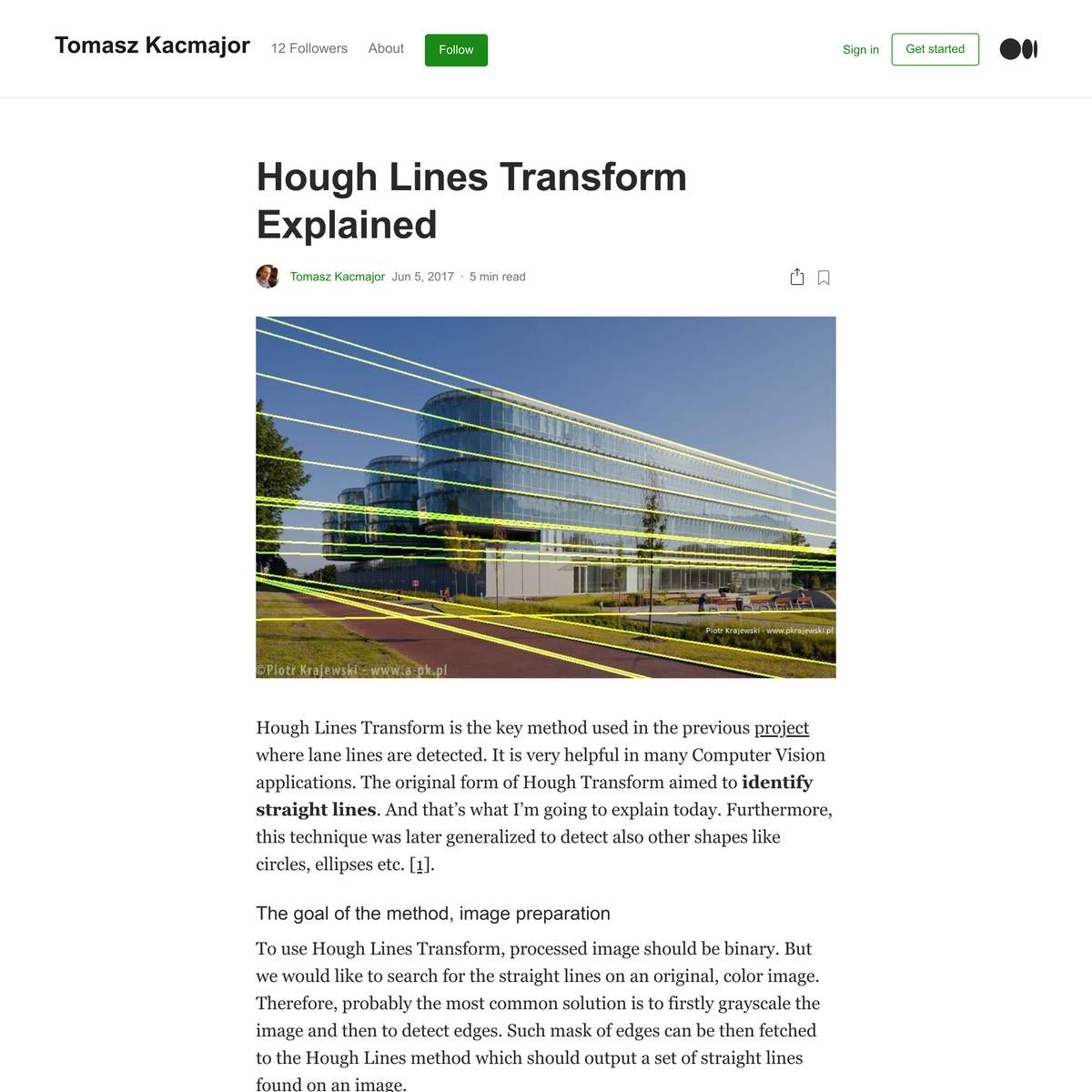


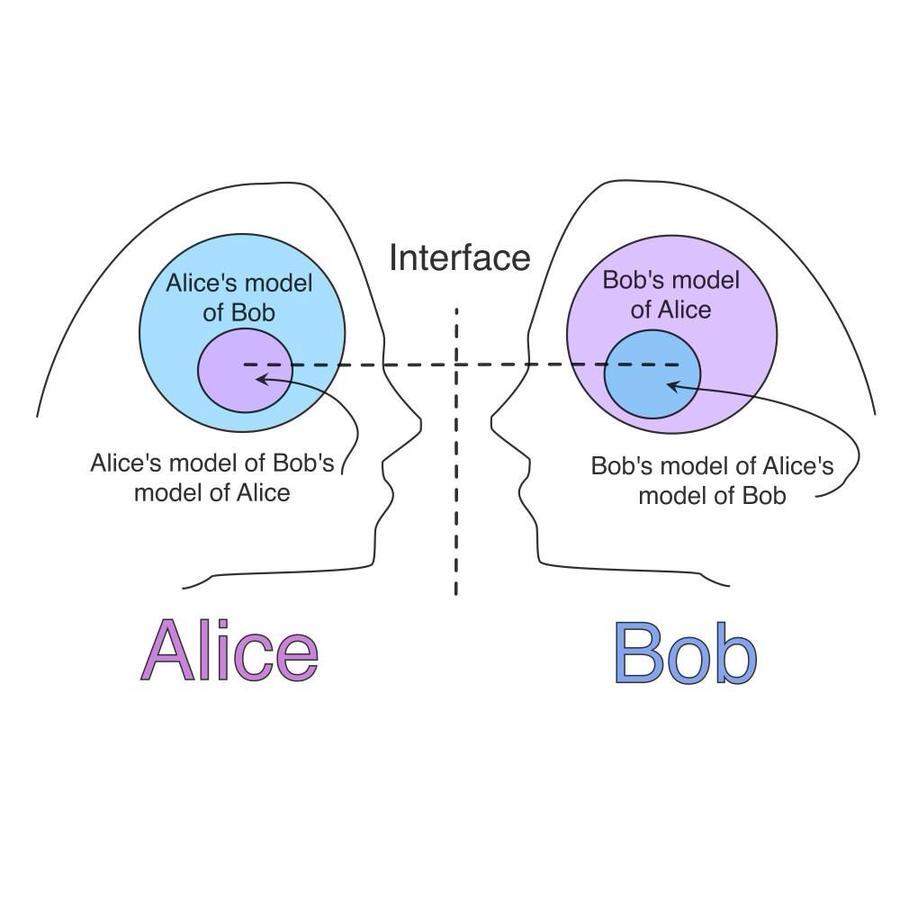





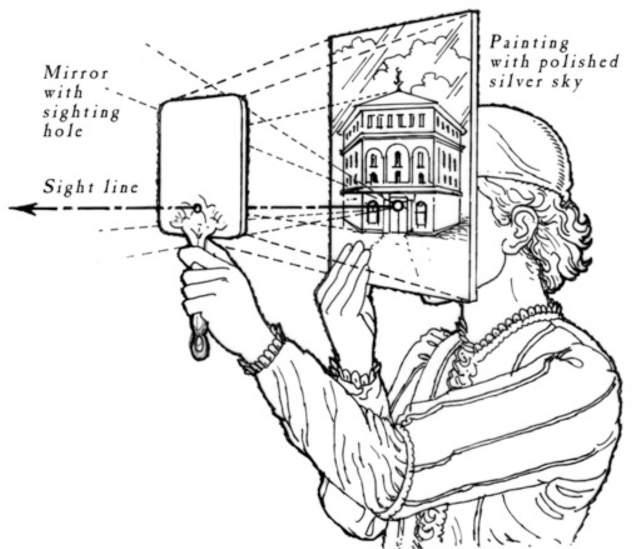


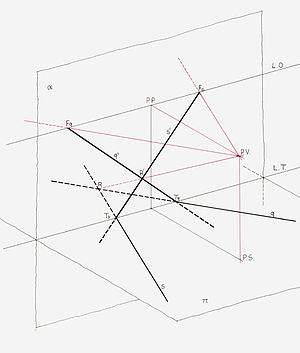


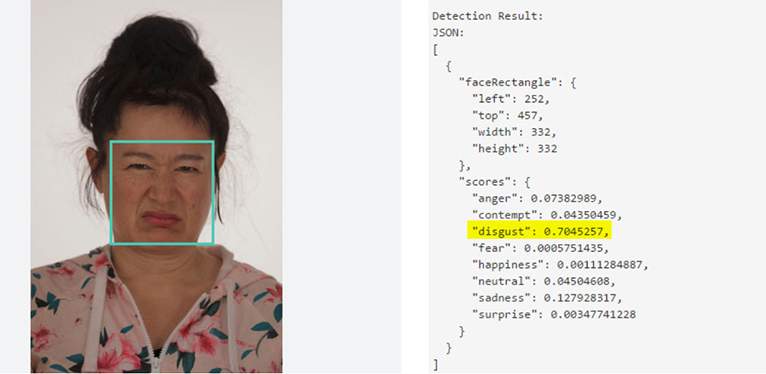


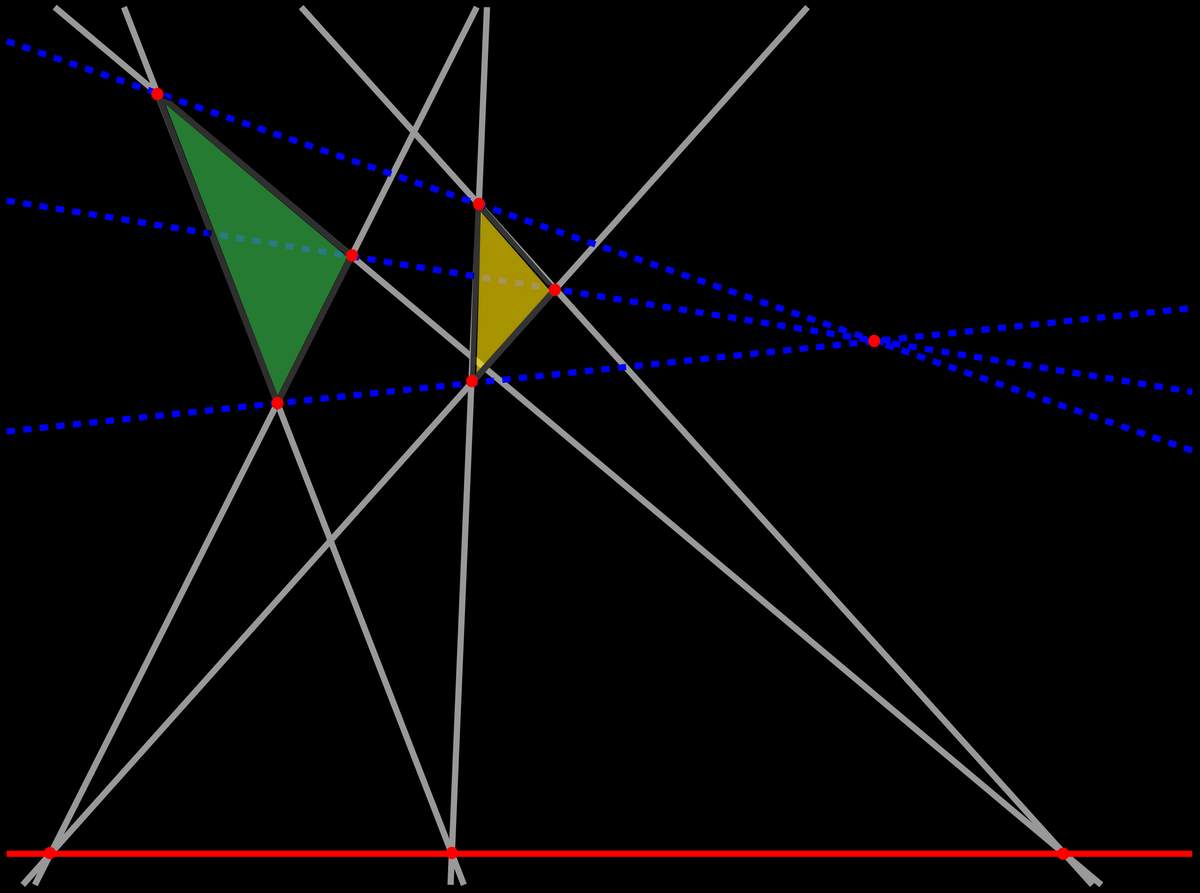











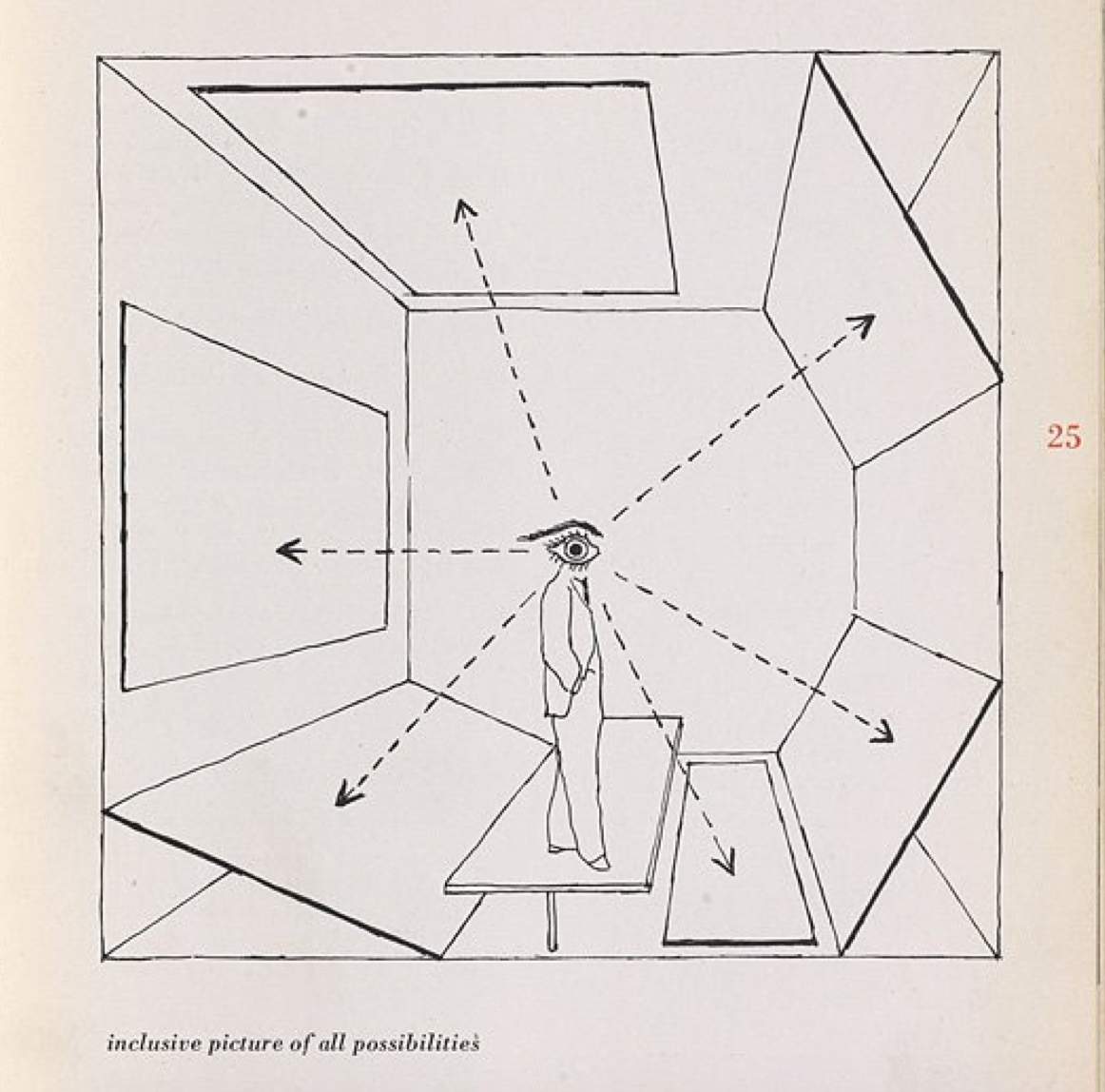


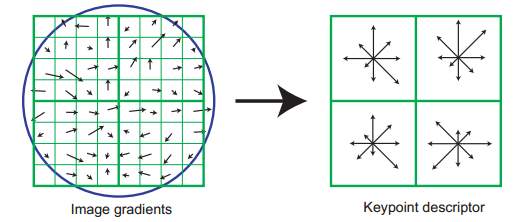




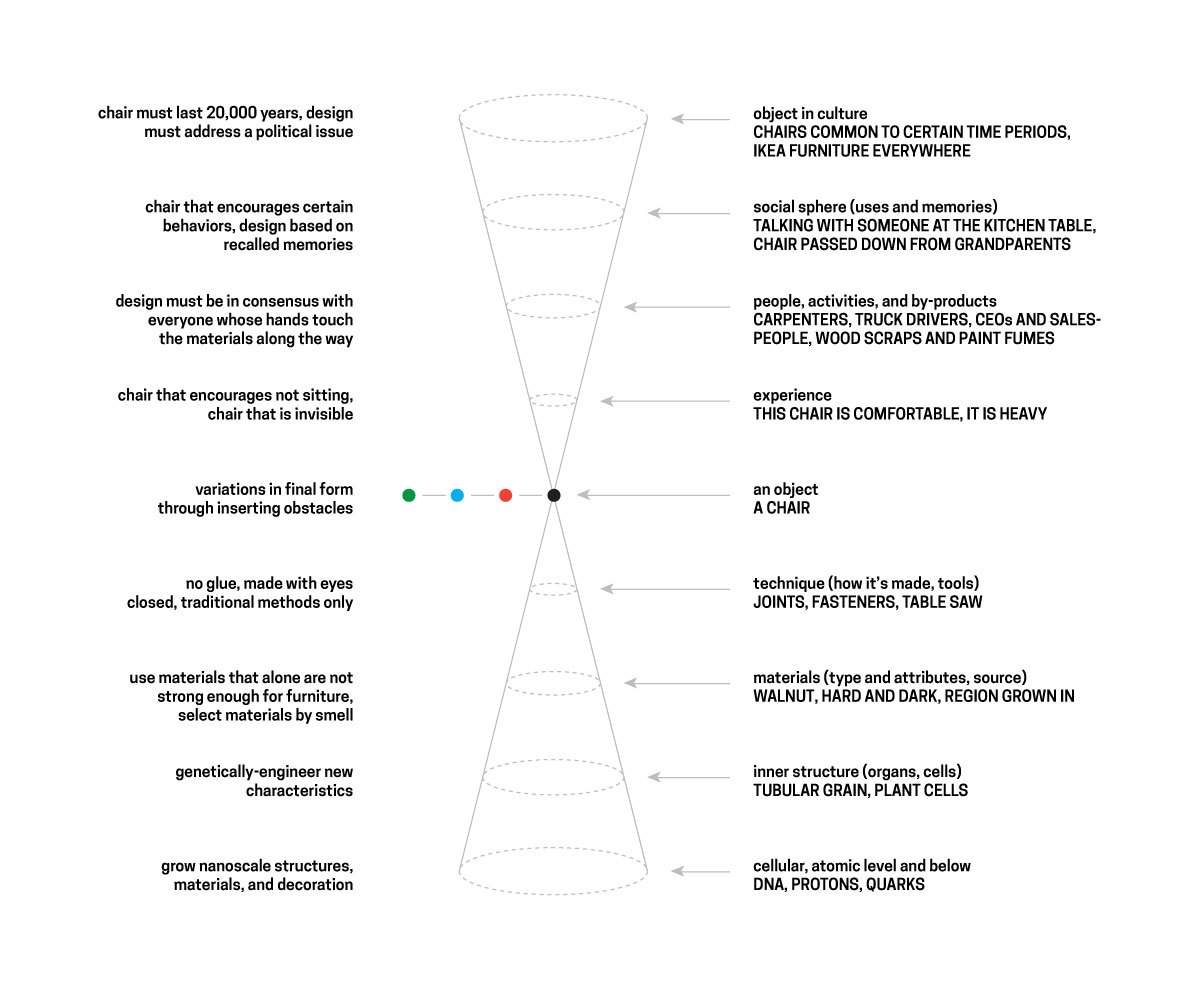


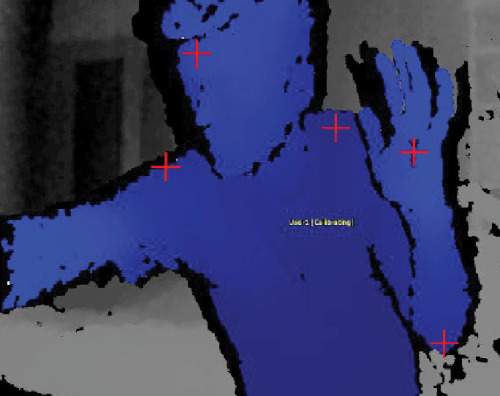


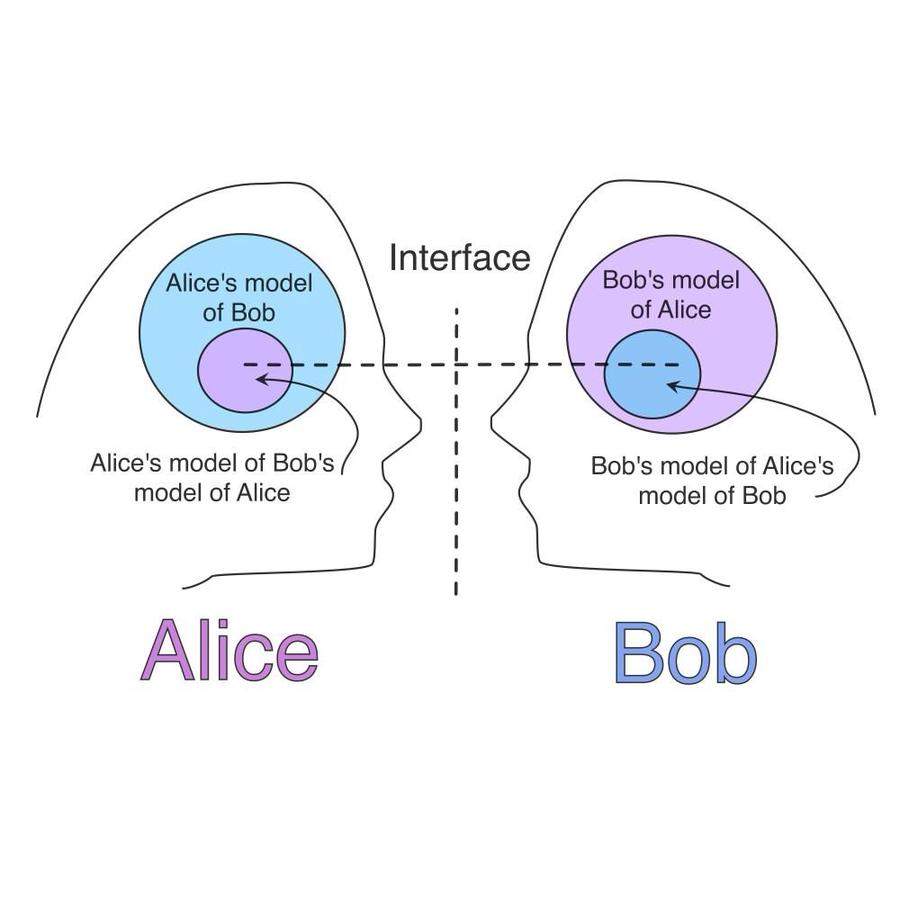
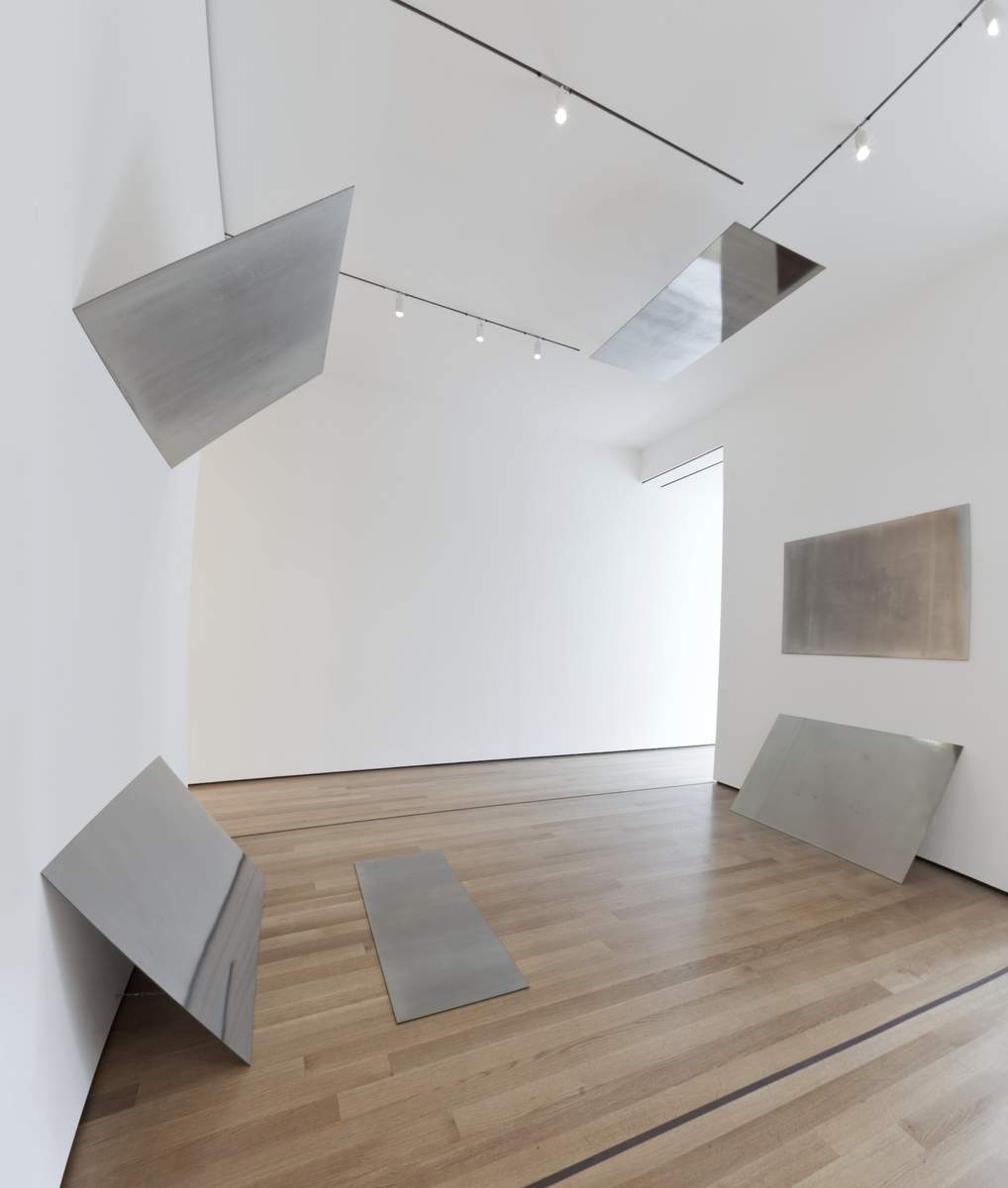
Seeing is superseded by calculating probabilities. Vision loses importance and is replaced by filtering, decrypting, and pattern recognition.
Seeing is superseded by calculating probabilities. Vision loses importance and is replaced by filtering, decrypting, and pattern recognition.
Seeing is superseded by calculating probabilities. Vision loses importance and is replaced by filtering, decrypting, and pattern recognition.
It is comparatively easy to make computers exhibit adult level performance on intelligence tests or playing checkers, and difficult or impossible to give them the skills of a one-year-old when it comes to perception and mobility.
It is comparatively easy to make computers exhibit adult level performance on intelligence tests or playing checkers, and difficult or impossible to give them the skills of a one-year-old when it comes to perception and mobility.
It is comparatively easy to make computers exhibit adult level performance on intelligence tests or playing checkers, and difficult or impossible to give them the skills of a one-year-old when it comes to perception and mobility.